Research on Reliability of Thermal Fuse Protecting Air Conditioner Electric Heater
Summary: Thermal fuses are an indispensable protective component in various electrical and electronic products. At the same time of widespread application, the thermal fuse itself inevitably exposes some problems and needs to continuously improve its reliability.
introduction: The thermal fuse is also called a thermal fuse and is a temperature-inductive circuit cut-off device. The thermal fuse can sense the overheating of electrical products and electronic products under abnormal working conditions, thereby cutting off the circuit to avoid fire. The thermal fuse is mostly used in household or similar electrical appliances, and its use is extensive, and is an indispensable key component in household and commercial electrical appliances and electronic products. The thermal fuse described in this paper is a cylindrical fuse-shaped fuse body with a heat-sensitive pellet (organic compound) as a heat-sensitive material capable of carrying a large current (6A to 25A). In fact, the object map is shown in Figure 1.

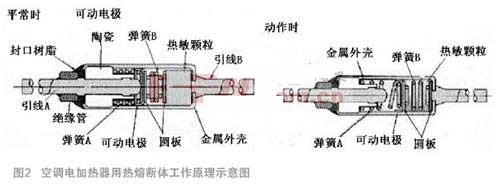
According to the "pre-action wire - movable electrode - metal shell - to-wire through current" sequence, the temperature rises and the heat-sensitive pellet melts when it senses heat. After the heat-sensitive pellet is melted, the spring is stretched, and the movable contact is separated from the wire end to cut off the current (see Figure 2).
 The hot fuse is installed in series as an element in the working circuit of the electrical appliances. In addition to the timely disconnection in the event of an abnormality, it should maintain good electrical conductivity under normal conditions, as close as possible to a wire. If the resistance value is too large, or even the fault is disconnected, it will inevitably affect the whole working circuit. Therefore, the reliability of hot fuses is very important.
The hot fuse is installed in series as an element in the working circuit of the electrical appliances. In addition to the timely disconnection in the event of an abnormality, it should maintain good electrical conductivity under normal conditions, as close as possible to a wire. If the resistance value is too large, or even the fault is disconnected, it will inevitably affect the whole working circuit. Therefore, the reliability of hot fuses is very important.
After the failure of the open circuit of the electric heating fuse of the air conditioner is found, there are some cases that are not caused by overheating of the working environment. That is to say, the fuse link has been disconnected when the design protection temperature is not reached, causing the electric heating working circuit to be disconnected, indicating that the reliability of the fuse body itself has certain defects. This paper mainly makes some research and analysis on such problems.
1 fuse body heat sensitive pill
1.1 Characteristics of the fuse link
Characteristic parameters of the thermal fuse:
1, rated operating temperature (Tf): the temperature at which the conductive state of the thermal fuse changes;
2, the maximum overload current (Im): the maximum current that the thermal fuse can withstand;
3, maintaining the temperature (Th, Tc): the maximum allowable temperature of the thermal fuse in the rated current, no change in the conductive state within 168 hours;
4, the limit temperature (Tm): the maximum temperature that can not be turned on again after the thermal fuse is activated;
5, action accuracy: according to the standard requirements, the operating temperature range of the thermal fuse.
When the air conditioner electric heating fuse is selected, it is necessary to determine the operating temperature range, which is Tf-10~Tf. In general, the rated temperature of the thermal link should be 25 ° C higher than the maximum temperature actually used.
1.2 Effect of ambient temperature on heat sensitive pills
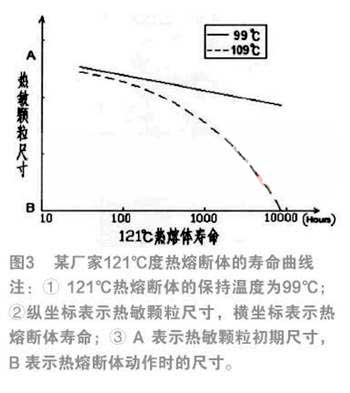
The service life of the hot fuse is closely related to the ambient temperature of the long-term use of the hot fuse. The closer the ambient temperature is to the operating temperature, the more severe the thermal aging of the heat-sensitive pellets and the shorter the service life of the thermal fuses. In particular, when the ambient temperature exceeds the holding temperature of the thermal fuse, the service life of the thermal fuse is drastically shortened. Figure 3 shows the service life curve of a manufacturer's 121 °C thermal fuse at 109 °C and 99 °C.
1.3 Test comparison
A 121 ° C fuse-link produced by a manufacturer on the market was selected as a sample, and the height of the heat-sensitive pellet was measured. High temperature baking was carried out in an oven at different temperatures for 30 min, and then the height of the heat-sensitive pellet after baking was measured and compared with the original temperature.
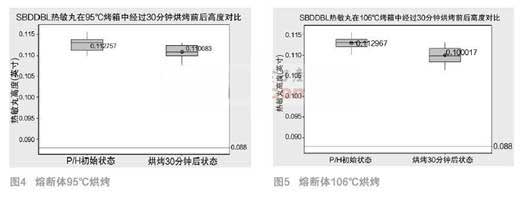
The sample of the fuse 1 was baked in a red box at 95 ° C for 30 min, and the height of the heat-sensitive pellet was compared as shown in FIG. 4 .
The No. 2 fuse sample was baked in a 106 ° C oven for 30 min, and the height of the heat sensitive pellet was compared as shown in Figure 5.
By comparison, it can be found that the fuselage of the manufacturer has substantially no change in height when baked at a high temperature of 95 °C. After the high temperature baking at 106 °C, the height has been significantly reduced, indicating that the heat sensitive pellets have shown signs of obvious melting under this condition, but at this time they are still far from reaching their rated operating temperature. At the same time, we use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the No. 2 fuse-link, and found that it has been opened, and the state after X-ray is shown in Figure 6.
In the actual electric heating production assembly process, the fuse body often has to undergo high temperature processes such as welding, baking and heat shrink tubing, which will inevitably be affected. Therefore, when performing these procedures, it is important to pay attention to the protection of the fuse:
2) The thermal fuse can splicing wires or terminals.
If the splicing process is unreliable, high resistance will be generated, which will cause a sudden increase in the amount of heat generated by the power, which eventually causes the heat sensitive pellet to melt abnormally.
3) When applying resin molding or heat shrinkable sleeve, the temperature on the body of the thermal fuse should be controlled to ensure that its volume will not shrink during processing, so as not to affect its reliability.
2 Mechanical structure of the fuse
2.1 Internal structure of the fuse
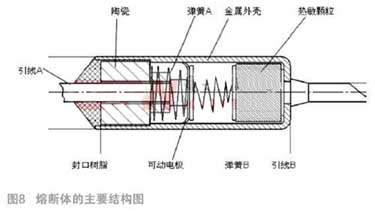
The working principle of the electric heating fuse link has been described above. The heat sensitive pellet is the key, but the final protective action and normal conduction are done by its internal mechanical structure. At present, its design mainly adopts the structure shown in Figure 7, and the manufacturers are slightly different, but the overall is similar. Insulation cylinders, springs, movable electrodes (also known as star contacts), circular plates and heat-sensitive pills are assembled in the metal shell, and the opening part of the metal shell is completely sealed with sealing materials.
Spring, as the power source of mechanical force, should be in a compressed state after normal assembly. At the same time, the star contact piece will remain in a vertical state due to the tension of the springs on both sides and will be in contact with the metal casing. The contact piece itself is small and thin, the material is soft, and the area of the contact metal casing is limited. Therefore, high requirements are imposed on its molding process and assembly process, and we have to doubt its reliability.
 2.2 Analysis of abnormal open circuit of fuse link
2.2 Analysis of abnormal open circuit of fuse link
The thermal fuses produced by a manufacturer have experienced several single-open faults during customer use, and there are no harsh conditions such as high temperature and high current during use. X-ray examination also found that the fuse body heat-sensitive pellet did not melt, indicating that there was a problem with the internal conduction loop of the fuse body itself.
Comparing normal and defective products, we can easily find the following problems:
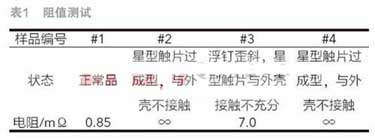
a. No. 2 and No. 4 samples have been molded, they have been separated from the metal casing, and the normal conduction circuit of the fuse is cut off here;
b. The electrode of sample No. 3 is skewed, the contact between the star contact and the outer casing is insufficient, and the contact surface between the electrode and the lead is also smaller than the normal product.
The test is conducted but the resistance is larger than normal (as shown in Table 1).
After analysis, the cause of the fuse body abnormality is caused by poor processing of the star contact (overmolding) and skewing of the floating electrode assembly. It shows that the manufacturer's production and processing technology and design have certain defects, and can not guarantee the consistency of its products. The following adjustments can be made from the design and internal size control to improve:
1) The inner diameter of the ceramic cap is designed to be narrowed, and the clearance tolerance between the ceramic inner circle and the floating nail is narrowed to avoid the occurrence of floating electrode skew;
2) Before the factory, the resistance resistance test range is tightened, and the contact between the star contact piece and the outer casing caused by the skew of the floating nail is detected and removed;
3) Change the size of the star contact piece, widen the eight-claw reed, increase the contact area with the metal casing, and improve reliability.
3 Conclusion
1) The reliability of the fuse body heat-sensitive pellets is affected by the ambient temperature. Even if the designed operating temperature is not reached, long-time high-temperature baking may cause the heat-sensitive pellets to melt. Fuse manufacturers should consider appropriate optimization, while ensuring sensitivity, but also taking into account high temperature stability; As the electric heating component, the fuse body should also pay attention to the high temperature protection during the assembly process, and the resistance value of the wire bonding part should also be controlled.
2) The star contact of the fuse link is a relatively fragile component of the mechanical structure. There is a high requirement for the processing technology, and no over-forming phenomenon can occur. At the same time, in the size design, it should be considered to ensure sufficient contact with the metal casing.
3) The tolerances of the components inside the fuse-link should be as strict as possible according to the requirements. Otherwise, problems such as floating electrode skew will inevitably occur.
introduction: The thermal fuse is also called a thermal fuse and is a temperature-inductive circuit cut-off device. The thermal fuse can sense the overheating of electrical products and electronic products under abnormal working conditions, thereby cutting off the circuit to avoid fire. The thermal fuse is mostly used in household or similar electrical appliances, and its use is extensive, and is an indispensable key component in household and commercial electrical appliances and electronic products. The thermal fuse described in this paper is a cylindrical fuse-shaped fuse body with a heat-sensitive pellet (organic compound) as a heat-sensitive material capable of carrying a large current (6A to 25A). In fact, the object map is shown in Figure 1.

According to the "pre-action wire - movable electrode - metal shell - to-wire through current" sequence, the temperature rises and the heat-sensitive pellet melts when it senses heat. After the heat-sensitive pellet is melted, the spring is stretched, and the movable contact is separated from the wire end to cut off the current (see Figure 2).

After the failure of the open circuit of the electric heating fuse of the air conditioner is found, there are some cases that are not caused by overheating of the working environment. That is to say, the fuse link has been disconnected when the design protection temperature is not reached, causing the electric heating working circuit to be disconnected, indicating that the reliability of the fuse body itself has certain defects. This paper mainly makes some research and analysis on such problems.
1 fuse body heat sensitive pill
1.1 Characteristics of the fuse link
Characteristic parameters of the thermal fuse:
1, rated operating temperature (Tf): the temperature at which the conductive state of the thermal fuse changes;
2, the maximum overload current (Im): the maximum current that the thermal fuse can withstand;
3, maintaining the temperature (Th, Tc): the maximum allowable temperature of the thermal fuse in the rated current, no change in the conductive state within 168 hours;
4, the limit temperature (Tm): the maximum temperature that can not be turned on again after the thermal fuse is activated;
5, action accuracy: according to the standard requirements, the operating temperature range of the thermal fuse.
When the air conditioner electric heating fuse is selected, it is necessary to determine the operating temperature range, which is Tf-10~Tf. In general, the rated temperature of the thermal link should be 25 ° C higher than the maximum temperature actually used.
1.2 Effect of ambient temperature on heat sensitive pills
The service life of the hot fuse is closely related to the ambient temperature of the long-term use of the hot fuse. The closer the ambient temperature is to the operating temperature, the more severe the thermal aging of the heat-sensitive pellets and the shorter the service life of the thermal fuses. In particular, when the ambient temperature exceeds the holding temperature of the thermal fuse, the service life of the thermal fuse is drastically shortened. Figure 3 shows the service life curve of a manufacturer's 121 °C thermal fuse at 109 °C and 99 °C.

1.3 Test comparison
A 121 ° C fuse-link produced by a manufacturer on the market was selected as a sample, and the height of the heat-sensitive pellet was measured. High temperature baking was carried out in an oven at different temperatures for 30 min, and then the height of the heat-sensitive pellet after baking was measured and compared with the original temperature.
The sample of the fuse 1 was baked in a red box at 95 ° C for 30 min, and the height of the heat-sensitive pellet was compared as shown in FIG. 4 .
The No. 2 fuse sample was baked in a 106 ° C oven for 30 min, and the height of the heat sensitive pellet was compared as shown in Figure 5.

By comparison, it can be found that the fuselage of the manufacturer has substantially no change in height when baked at a high temperature of 95 °C. After the high temperature baking at 106 °C, the height has been significantly reduced, indicating that the heat sensitive pellets have shown signs of obvious melting under this condition, but at this time they are still far from reaching their rated operating temperature. At the same time, we use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the No. 2 fuse-link, and found that it has been opened, and the state after X-ray is shown in Figure 6.
In the actual electric heating production assembly process, the fuse body often has to undergo high temperature processes such as welding, baking and heat shrink tubing, which will inevitably be affected. Therefore, when performing these procedures, it is important to pay attention to the protection of the fuse:
2) The thermal fuse can splicing wires or terminals.
If the splicing process is unreliable, high resistance will be generated, which will cause a sudden increase in the amount of heat generated by the power, which eventually causes the heat sensitive pellet to melt abnormally.
3) When applying resin molding or heat shrinkable sleeve, the temperature on the body of the thermal fuse should be controlled to ensure that its volume will not shrink during processing, so as not to affect its reliability.
2 Mechanical structure of the fuse
2.1 Internal structure of the fuse
The working principle of the electric heating fuse link has been described above. The heat sensitive pellet is the key, but the final protective action and normal conduction are done by its internal mechanical structure. At present, its design mainly adopts the structure shown in Figure 7, and the manufacturers are slightly different, but the overall is similar. Insulation cylinders, springs, movable electrodes (also known as star contacts), circular plates and heat-sensitive pills are assembled in the metal shell, and the opening part of the metal shell is completely sealed with sealing materials.
Spring, as the power source of mechanical force, should be in a compressed state after normal assembly. At the same time, the star contact piece will remain in a vertical state due to the tension of the springs on both sides and will be in contact with the metal casing. The contact piece itself is small and thin, the material is soft, and the area of the contact metal casing is limited. Therefore, high requirements are imposed on its molding process and assembly process, and we have to doubt its reliability.

The thermal fuses produced by a manufacturer have experienced several single-open faults during customer use, and there are no harsh conditions such as high temperature and high current during use. X-ray examination also found that the fuse body heat-sensitive pellet did not melt, indicating that there was a problem with the internal conduction loop of the fuse body itself.
Comparing normal and defective products, we can easily find the following problems:
a. No. 2 and No. 4 samples have been molded, they have been separated from the metal casing, and the normal conduction circuit of the fuse is cut off here;
b. The electrode of sample No. 3 is skewed, the contact between the star contact and the outer casing is insufficient, and the contact surface between the electrode and the lead is also smaller than the normal product.
The test is conducted but the resistance is larger than normal (as shown in Table 1).

After analysis, the cause of the fuse body abnormality is caused by poor processing of the star contact (overmolding) and skewing of the floating electrode assembly. It shows that the manufacturer's production and processing technology and design have certain defects, and can not guarantee the consistency of its products. The following adjustments can be made from the design and internal size control to improve:
1) The inner diameter of the ceramic cap is designed to be narrowed, and the clearance tolerance between the ceramic inner circle and the floating nail is narrowed to avoid the occurrence of floating electrode skew;
2) Before the factory, the resistance resistance test range is tightened, and the contact between the star contact piece and the outer casing caused by the skew of the floating nail is detected and removed;
3) Change the size of the star contact piece, widen the eight-claw reed, increase the contact area with the metal casing, and improve reliability.

3 Conclusion
1) The reliability of the fuse body heat-sensitive pellets is affected by the ambient temperature. Even if the designed operating temperature is not reached, long-time high-temperature baking may cause the heat-sensitive pellets to melt. Fuse manufacturers should consider appropriate optimization, while ensuring sensitivity, but also taking into account high temperature stability; As the electric heating component, the fuse body should also pay attention to the high temperature protection during the assembly process, and the resistance value of the wire bonding part should also be controlled.
2) The star contact of the fuse link is a relatively fragile component of the mechanical structure. There is a high requirement for the processing technology, and no over-forming phenomenon can occur. At the same time, in the size design, it should be considered to ensure sufficient contact with the metal casing.
3) The tolerances of the components inside the fuse-link should be as strict as possible according to the requirements. Otherwise, problems such as floating electrode skew will inevitably occur.





